UNPACKING TEACHER LEADERSHIP
“If your actions inspire others to dream more, learn more, do more and become more, you are a leader.“
John Quincy Adams
What are Teacher Leadership Roles?
Whether in formal or informal leadership roles, strong teacher leaders are committed to the success of all students and willing to serve in a variety of roles to support their school/district. Read the brief by Harrison and Killion (2007) Ten Roles for Teacher Leaders for ideas on possible teacher leadership roles. Which of the roles mentioned would be feasible for your school/district?
The Impact: When Teachers Take the Lead in Schools
Teacher leadership can have a powerful impact on schools and student learning. According to the study School Leadership, Teachers’ Roles in School Decision-Making and Student Achievement (Ingersoll, et al., 2017), schools with higher levels of both instructional leadership and teacher leadership were found to have greater student achievement. The researchers reported aspects of instructional leadership that were most strongly related to student achievement, which included holding teachers to high professional standards for delivering instruction, effective school improvement teams, and fostering a shared vision for the school. The elements of teacher leadership found to be most strongly related to student achievement included teacher participation in both school improvement planning and establishing policies and procedures for student conduct. Additionally, a Wallace Foundation study (Leithwood et al., 2010), Collective Leadership Effects on Teachers and Students – Learning From Leadership, defined collective leadership as the influence that organizational members and stakeholders have in school decisions. They reported the following key findings regarding collective leadership in schools.
- Collective leadership has a stronger influence on student achievement than a more top-down approach.
- There is less collective leadership in low-performing schools than in high-performing schools.
- Higher-performing schools acknowledge greater influence by teacher teams, parents, and students.
- Principals and district leaders do not lose their influence as other leaders gain influence.
- Schools leaders primarily impact student achievement through their influence on teacher motivation and working conditions.
Connecting Teacher Leadership to the Four Sources of Efficacy
Teacher leadership is a valuable avenue for developing CTE because it provides educators with increased opportunities for mastery and vicarious experiences. As teachers participate in school/district decision-making, they are involved in mastery experiences that connect decisions and data. The feedback that happens between colleagues when there is teacher leadership creates a context for social persuasion and the sharing of experiences (Lewis, 2009). Teacher leadership also promotes a school climate that values and encourages teachers to be change agents, which creates opportunities for teachers to experience collaborative educational practices that not only build CTE but can lead to improved student outcomes.
Peter DeWitt (2017) states that through collective leadership, principals can enhance the instruction of teachers, build strong relationships with stakeholders, and deepen the collective learning of staff. Read DeWitt’s (2017) article Many Hands Make Light Work: How Collaborative Leadership Leads to Collective Efficacy that outlines how collaborative leadership leads to collective efficacy.
Reflection Questions
- What are the benefits of collaborative leadership?
- How does the sharing of tasks and responsibilities with other educators lead to greater collective efficacy?
Watch a segment (0.15-3:10) from the video What is a Teacher Leader? (EngageNY, 2014) and consider characteristics of a strong teacher leader.
What is a Teacher Leader? (0.15-3.10 min.)
Reflection Questions
- How is CTE being built through teacher leadership in this video?
- What are some of the roles and responsibilities teacher leaders have?
The Seven Dimensions of Teacher Leadership Practice (York-Barr & Duke, 2004)
Download a copy of the below chart.
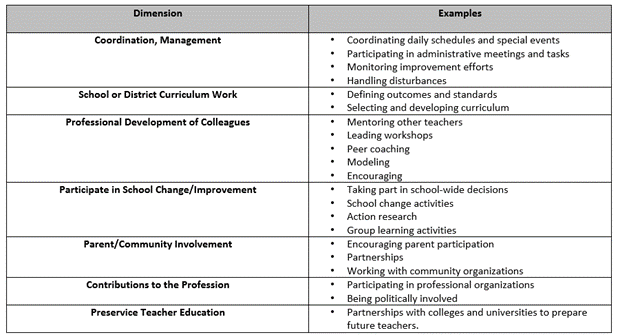
The Teacher Leader Self-Reflection Inventory (Tennessee Department of Education, 2004) can be used to examine the levels of teacher leadership practices that are used in a school/district. School leaders can use this inventory to determine areas of strength and opportunities for growth in their schools/districts. This inventory can also be revised and adapted to best meet the needs and practices of individual school settings.
Reflection Questions
- What would be the impact of strengthening teacher leadership in your school/district?
- What teacher leadership roles currently exist in your school/district?
- Are teacher leadership roles representative of all dimensions of teacher leadership practice? If not, how could those roles be expanded?
- How might your school/district encourage more collective leadership?

